9.7 Combining Mediation and Moderation
Mediation and moderation (Chapters 6 and 7) can occur in the same model. For example, the effect of age on newspaper reading time mediated by interest in politics can be different for females and males. In other words, the indirect effect is different for females and males.
If the indirect effect is different for females and males, at least one of the two direct effects (predictor on mediator or mediator on dependent variable) must be different for females and males. In Figure 9.16, the direct effect of age on interest in politics is moderated and as a consequence, indirect effects including this effect are moderated. This is called moderated mediation. In this example, sex is the moderator and interest in politics is the mediator.
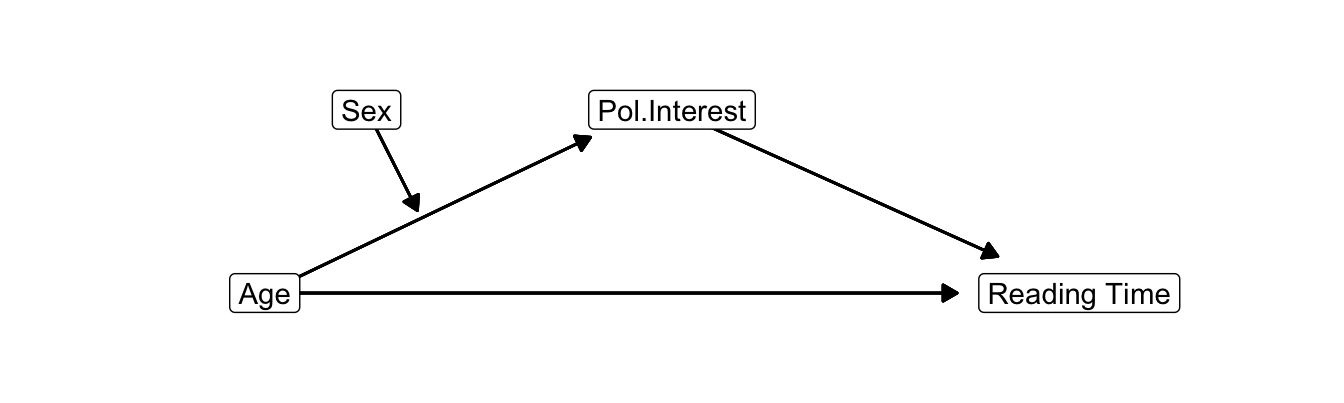
Figure 9.16: Causal diagram for interest in politics as mediator between age and newspaper reading time with sex as moderator of the effect of age on interest in politics.
Several models with more than one mediator or with moderated mediation can be estimated with PROCESS. For an overview of the models, see Appendix A in Hayes (2013). The models, however, are quite complex, so we leave them for enthusiasts.